Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, where we delve into the fundamental differences that distinguish these two cell types. This comprehensive guide, ‘Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet Answers,’ provides a thorough understanding of their structures, functions, and the processes that govern their existence.
Delving into the intricate world of cells, we unravel the secrets of prokaryotic cells, exploring their unique characteristics, including the absence of a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Conversely, we delve into the complexities of eukaryotic cells, showcasing their intricate organization, complete with a nucleus and an array of specialized organelles that orchestrate cellular functions.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Overview
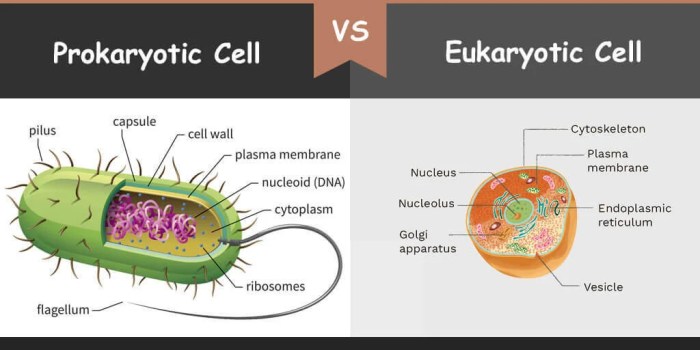
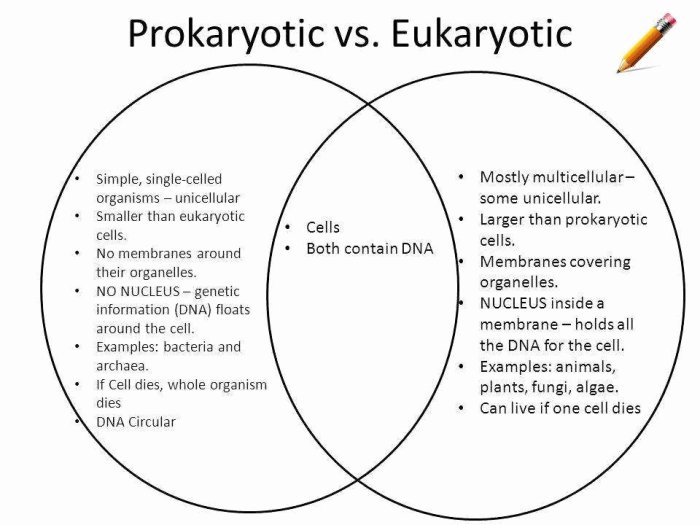
Cells are the basic units of life and come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells and lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, making them more complex and larger.
The table below compares the key characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Typically 1-10 micrometers | Typically 10-100 micrometers |
| Nucleus | No true nucleus, only a nucleoid region | Membrane-bound nucleus containing genetic material |
| Organelles | No membrane-bound organelles | Membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus |
| Ribosomes | 70S ribosomes | 80S ribosomes |
| Cell Division | Binary fission | Mitosis |
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
Prokaryotic cells have a simple structure, with most of the cell’s functions taking place in the cytoplasm. The cell membrane surrounds the cytoplasm and regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. The cytoplasm contains ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis, and a nucleoid region, which contains the cell’s genetic material.
Prokaryotic Cell Membrane
The prokaryotic cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. It also contains proteins that help to transport materials across the membrane.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains the cell’s organelles. The cytoplasm is where most of the cell’s metabolic activities take place.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small, round organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis. Ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm and are composed of RNA and protein.
Nucleoid
The nucleoid is the region of the cytoplasm that contains the cell’s genetic material. The nucleoid is not surrounded by a membrane.
Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet Answers
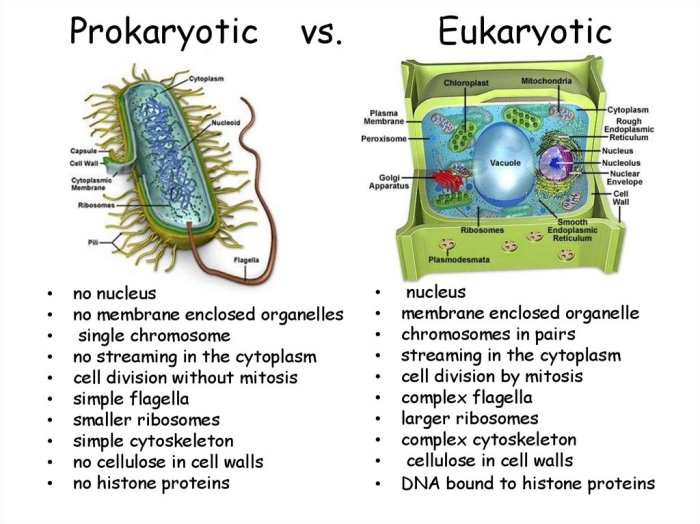
Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells and have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The cell membrane surrounds the cytoplasm and regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. The cytoplasm contains organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, which perform specific functions for the cell.
Eukaryotic Cell Membrane
The eukaryotic cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell. It also contains proteins that help to transport materials across the membrane.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains the cell’s organelles. The cytoplasm is where most of the cell’s metabolic activities take place.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material. The nucleus is the control center of the cell and directs the cell’s activities.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are small, bean-shaped organelles that are responsible for producing energy for the cell. Mitochondria are found in the cytoplasm and are composed of two membranes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum is found in the cytoplasm and is composed of two types: rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
Golgi Apparatus, Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells worksheet answers
The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened sacs that modifies and packages proteins. The Golgi apparatus is found in the cytoplasm and is composed of a series of cisternae.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the primary distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The presence of a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells sets them apart from prokaryotic cells, which lack these features.
How do prokaryotic cells reproduce?
Prokaryotic cells reproduce through binary fission, a simple process where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
What is the function of the mitochondria in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondria are the ‘powerhouses’ of eukaryotic cells, responsible for generating energy through cellular respiration.
