Label the diagram frog dissection – Label the Diagram: Frog Dissection offers a comprehensive exploration into the fascinating anatomy of frogs. Through a detailed and interactive guide, this dissection experience unveils the intricate structures and functions of this remarkable amphibian.
Immerse yourself in the wonders of frog biology as we delve into the intricacies of their organs, anatomical features, and comparative anatomy. Discover the educational value of dissection and the safety precautions to ensure a responsible and informative learning experience.
Frog Dissection: A Comprehensive Guide
Frog dissection is a fundamental exercise in biology education, providing students with hands-on experience in animal anatomy and physiology. This article provides a comprehensive guide to frog dissection, including a detailed diagram of the major organs, a step-by-step dissection procedure, an explanation of the functions of the anatomical structures, a comparison of frog anatomy to other vertebrates, a discussion of the educational applications of dissection, and safety precautions.
Diagram Components
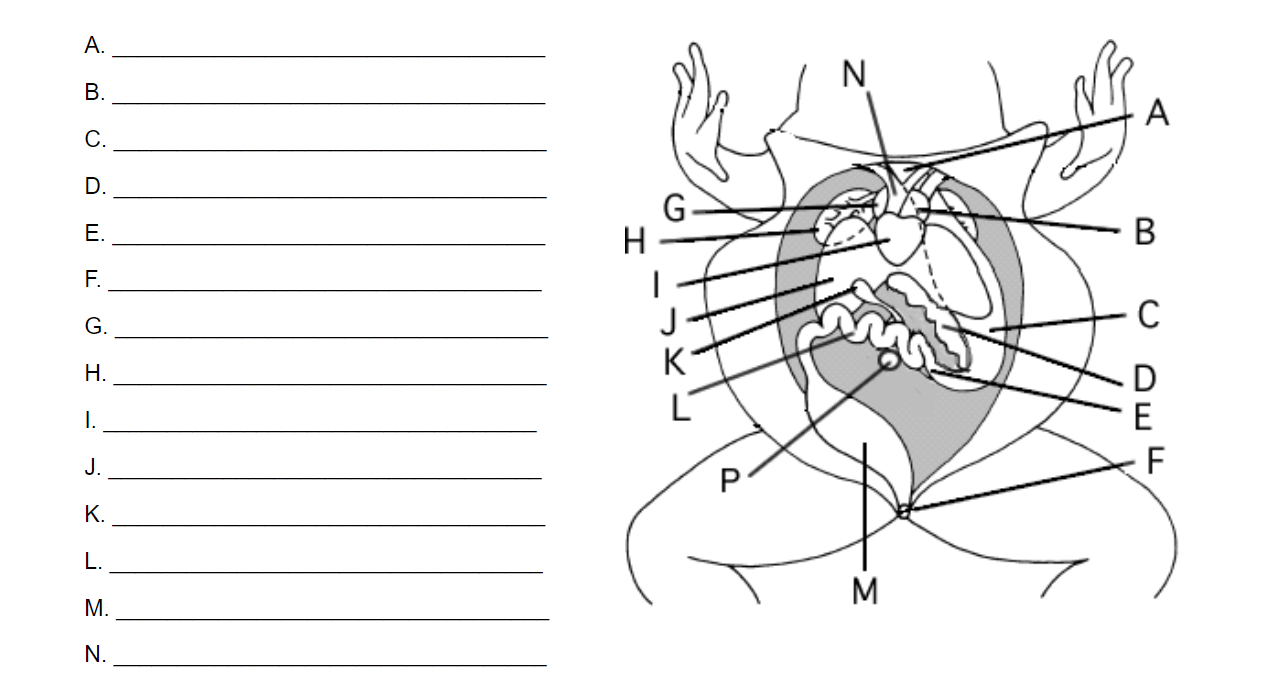
| Section | Organ | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Head | Brain | Controls the frog’s nervous system | [Image of frog brain] |
| Head | Eyes | Detect light and enable vision | [Image of frog eyes] |
| Head | Mouth | Ingests food and produces vocalizations | [Image of frog mouth] |
| Head | Ears | Detect sound waves and enable hearing | [Image of frog ears] |
| Thorax | Lungs | Facilitate gas exchange | [Image of frog lungs] |
| Thorax | Heart | Pumps blood throughout the body | [Image of frog heart] |
| Thorax | Liver | Processes nutrients and detoxifies the blood | [Image of frog liver] |
| Abdomen | Stomach | Digests food | [Image of frog stomach] |
| Abdomen | Intestines | Absorb nutrients from food | [Image of frog intestines] |
| Abdomen | Kidneys | Filter waste products from the blood | [Image of frog kidneys] |
| Abdomen | Reproductive organs | Produce and store gametes | [Image of frog reproductive organs] |
Dissection Procedure
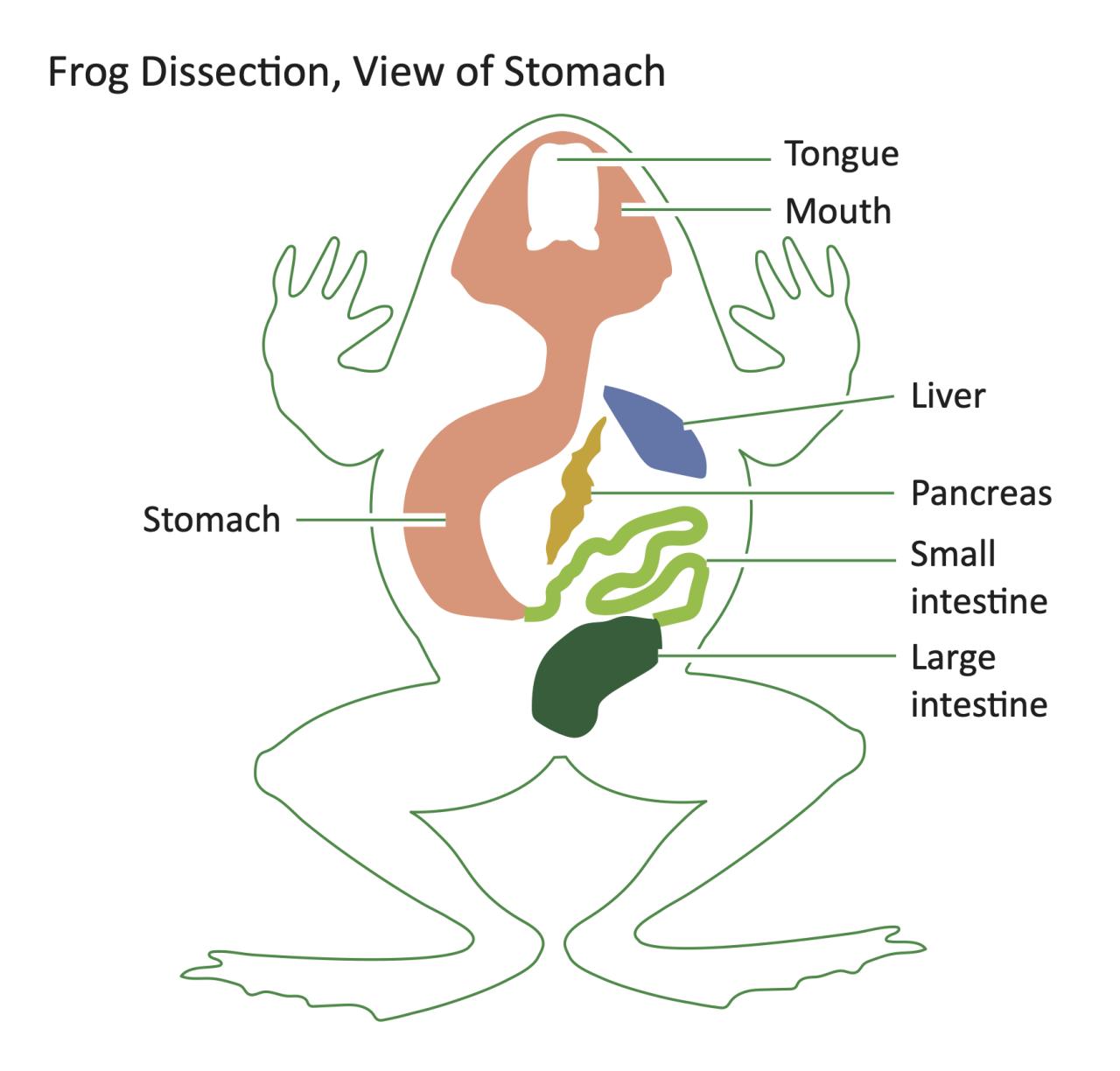
- Obtain a preserved frog specimen and place it on a dissection tray.
- Using a scalpel, make a ventral incision along the midline of the frog’s body, from the chin to the cloaca.
- Carefully open the body cavity and pin the skin flaps back to expose the internal organs.
- Identify the major organs of the frog, including the brain, lungs, heart, liver, stomach, intestines, kidneys, and reproductive organs.
- Observe the external and internal anatomy of each organ and note its function.
- Clean up the dissection area and dispose of the frog specimen and dissection materials properly.
Anatomical Structures: Label The Diagram Frog Dissection
- Brain:Controls the frog’s nervous system, including its behavior, movement, and sensory perception.
- Lungs:Facilitate gas exchange between the frog’s bloodstream and the environment.
- Heart:Pumps blood throughout the frog’s body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to its cells.
- Liver:Processes nutrients from food and detoxifies the blood.
- Stomach:Digests food and prepares it for absorption in the intestines.
- Intestines:Absorb nutrients from food and produce waste products.
- Kidneys:Filter waste products from the blood and produce urine.
- Reproductive organs:Produce and store gametes, enabling the frog to reproduce.
Comparative Anatomy
| Structure | Frog | Mammal | Bird | Reptile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | Small and simple | Large and complex | Intermediate in size and complexity | Small and simple |
| Lungs | Sac-like | Lobed | Air sacs | Sac-like |
| Heart | Three-chambered | Four-chambered | Four-chambered | Three-chambered |
| Liver | Large and bilobed | Large and multilobed | Small and bilobed | Large and bilobed |
| Stomach | Single-chambered | Multi-chambered | Gizzard and proventriculus | Single-chambered |
| Intestines | Relatively short | Very long | Short and coiled | Relatively short |
| Kidneys | Mesonephric | Metanephric | Metanephric | Mesonephric |
| Reproductive organs | External fertilization | Internal fertilization | Internal fertilization | External or internal fertilization |
Educational Applications
- Frog dissection provides students with a hands-on experience in animal anatomy and physiology.
- It helps students understand the structure and function of different organs and systems in the body.
- Frog dissection can be integrated into science curricula to enhance students’ understanding of biology and evolution.
- It can also foster critical thinking, problem-solving, and observation skills.
Safety Precautions
- Wear gloves and safety glasses when dissecting a frog.
- Handle the dissection materials carefully and avoid touching your face or mouth.
- Use sharp instruments with caution and dispose of them properly.
- Clean up the dissection area thoroughly after use.
- Dispose of the frog specimen and dissection materials according to your institution’s guidelines.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the purpose of labeling a frog dissection diagram?
Labeling a frog dissection diagram helps students identify and understand the various organs and structures of a frog, providing a visual representation of its anatomy.
What safety precautions should be taken during a frog dissection?
Wear gloves, safety goggles, and a lab coat. Use sharp dissection tools carefully and dispose of all dissection materials properly.
How can frog dissection enhance students’ understanding of biology?
Frog dissection provides hands-on experience, allowing students to observe the internal structures of an organism and gain a deeper understanding of organ function and interdependence.