To analyze the characteristics and performance of the brakes – To analyze the characteristics and performance of brakes is a crucial aspect of ensuring vehicle safety and efficiency. This comprehensive analysis involves examining the braking system’s components, evaluating brake performance, understanding brake characteristics, establishing testing procedures, and interpreting data to identify areas for improvement.
By delving into the intricacies of brake systems, we can optimize their effectiveness and contribute to safer and more reliable vehicles.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Braking System Overview
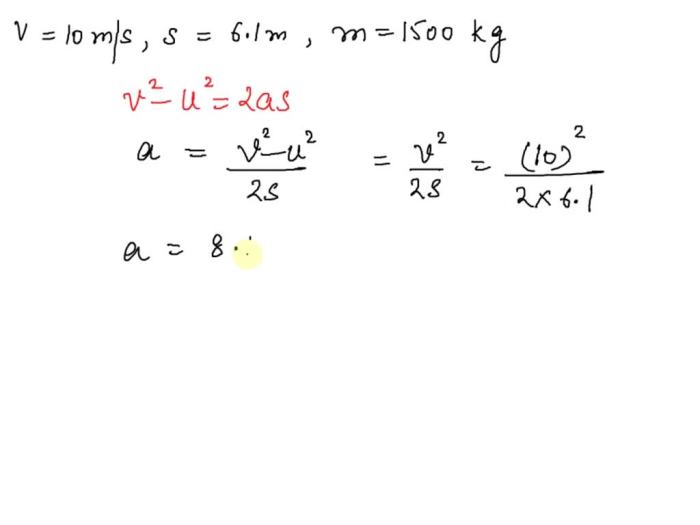
Braking systems are essential for controlling vehicle motion and ensuring passenger safety. They consist of several components working together to convert kinetic energy into heat and friction, slowing down or stopping the vehicle.
Primary Components
- Brake pedal: Initiates the braking process when depressed.
- Master cylinder: Converts mechanical force from the pedal into hydraulic pressure.
- Brake lines: Transfer hydraulic pressure to the brake calipers.
- Brake calipers: House brake pads that clamp down on brake rotors to generate friction.
- Brake rotors: Dissipate heat generated during braking.
Types of Braking Systems
- Disc brakes: Utilize brake pads and rotors to generate friction.
- Drum brakes: Use brake shoes to press against the inner surface of a rotating drum.
- Hydraulic brakes: Rely on hydraulic fluid to transmit pressure from the master cylinder to the brake calipers.
- Electric brakes: Use electric motors to engage the brake pads.
Brake Performance Analysis
Methods for Measuring Brake Performance
- Stopping distance: Distance traveled by the vehicle from the moment the brake pedal is applied to the point where it comes to a complete stop.
- Brake fade: Reduction in braking effectiveness due to prolonged or repeated braking.
- Coefficient of friction: Ratio of the force of friction between the brake pads and rotors to the normal force applied.
Factors Affecting Brake Performance
- Friction: Determined by the materials used in the brake pads and rotors.
- Temperature: High temperatures can reduce brake effectiveness due to thermal fade.
- Wear: Brake pads and rotors wear over time, affecting their friction and performance.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Stopping distance
- Coefficient of friction
- Brake fade
- Brake pedal feel
Brake Characteristics: To Analyze The Characteristics And Performance Of The Brakes

Materials Used in Brake Pads and Rotors
- Ceramic: High friction and durability, but expensive.
- Organic: Lower friction and durability than ceramic, but quieter and less expensive.
- Semi-metallic: Blend of organic and metallic materials, offering a balance of performance and cost.
- Metallic: High friction and durability, but can be noisy and wear rotors faster.
Impact of Material Properties
- Friction: Determined by the coefficient of friction between the brake pads and rotors.
- Durability: Resistance to wear and tear over time.
- Noise: Generated by the friction between the brake pads and rotors.
- Rotor wear: Impact on the longevity of the brake rotors.
Relationship to Vehicle Safety
- Shorter stopping distances improve vehicle safety by reducing the risk of collisions.
- Consistent brake performance enhances driver confidence and control.
- Reliable brakes are essential for avoiding accidents and protecting occupants.
Brake Testing Procedures
Comprehensive Test Plan
- Define test objectives and performance criteria.
- Select representative vehicles and brake systems.
- Establish testing conditions (e.g., temperature, road surface).
- Identify performance indicators to be measured.
Equipment and Instrumentation
- Accelerometer
- Distance measurement system
- Temperature sensors
- Data acquisition system
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Prepare vehicle and test environment.
- Mount sensors and connect instrumentation.
- Conduct a series of braking tests.
- Record and analyze data.
- Repeat tests under varying conditions.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data Analysis Plan, To analyze the characteristics and performance of the brakes
- Define statistical methods for data analysis.
- Identify variables to be analyzed and relationships to be explored.
- Establish criteria for interpreting results.
Statistical Methods
- Regression analysis
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Correlation analysis
Interpreting Brake Performance Data
- Identify trends and patterns in brake performance.
- Determine the effects of different variables on brake effectiveness.
- Draw conclusions based on statistical analysis.
FAQs
What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) for evaluating brake effectiveness?
KPIs include stopping distance, fade resistance, pedal feel, and noise generation.
How do material properties impact brake performance?
Material properties such as friction coefficient, thermal conductivity, and wear resistance influence brake performance and durability.
What are the common methods for measuring brake performance?
Methods include dynamometer testing, vehicle testing, and data acquisition systems.