Como se divide el antiguo testamento – The Old Testament, a cornerstone of religious and historical literature, is a complex and multifaceted work. Its intricate structure, encompassing various divisions, has shaped its interpretation and understanding throughout history. This guide delves into the diverse ways in which the Old Testament has been divided, exploring their historical, literary, canonical, modern, and comparative dimensions.
From the traditional Jewish tripartite division of Torah, Nevi’im, and Ketuvim to the modern division into chapters and verses, each division offers a unique lens through which to appreciate the richness and complexity of the Old Testament.
Historical Divisions

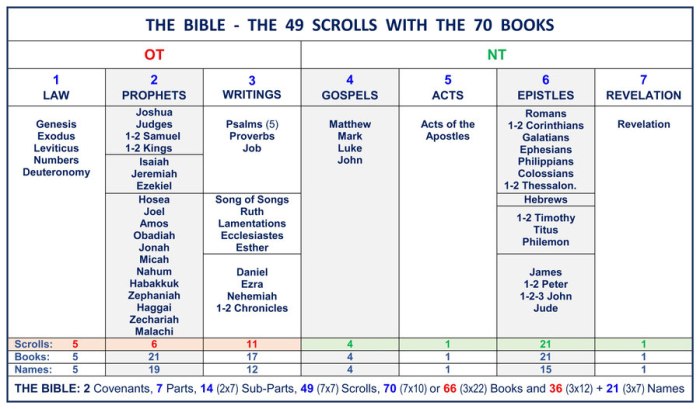
The Old Testament is traditionally divided into three main sections: Torah, Nevi’im, and Ketuvim. This division is based on the historical development of the Hebrew Bible and reflects the different literary genres and historical contexts of the texts.
Torah
The Torah, also known as the Pentateuch, comprises the first five books of the Old Testament: Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, and Deuteronomy. These books contain the foundational narratives of the Israelites, including the creation of the world, the patriarchs and matriarchs, the Exodus from Egypt, and the giving of the Law at Mount Sinai.
The Torah is considered the most sacred part of the Old Testament and is the basis for Jewish religious law and practice.
Nevi’im
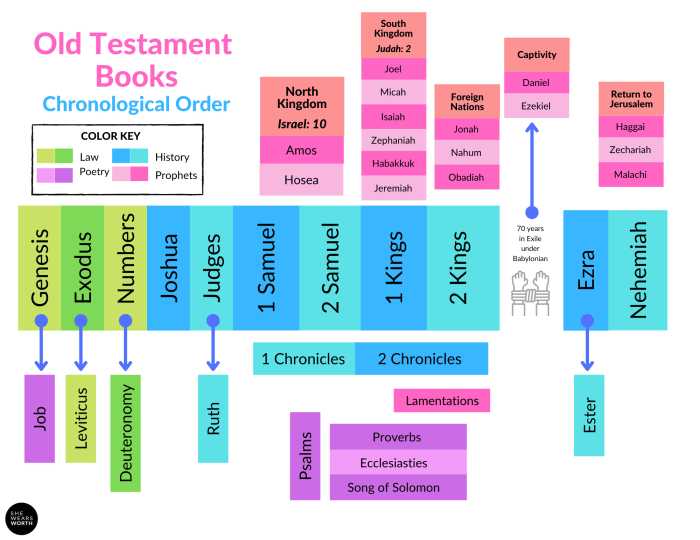
The Nevi’im, meaning “prophets,” includes the historical books (Joshua, Judges, Samuel, and Kings) and the prophetic books (Isaiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel, and the Twelve Minor Prophets). The historical books recount the history of the Israelites from the conquest of Canaan to the Babylonian exile, while the prophetic books contain the oracles and teachings of the prophets, who spoke out on behalf of God and addressed the social, political, and religious issues of their time.
Ketuvim
The Ketuvim, meaning “writings,” is a collection of diverse literary genres, including poetry (Psalms, Proverbs, Job), wisdom literature (Ecclesiastes, Song of Solomon), and historical narratives (Ruth, Esther, Chronicles). The Ketuvim reflects the diversity of thought and experience within ancient Israel and includes some of the most beloved and influential texts of the Old Testament.
Literary Divisions
The Old Testament is also divided into three main literary genres: poetic, prophetic, and wisdom literature. Each genre has its own distinct characteristics and themes.
Poetic Literature, Como se divide el antiguo testamento
Poetic literature includes Psalms, Proverbs, Job, Song of Solomon, Ecclesiastes, and Lamentations. These books are characterized by their use of vivid imagery, metaphor, and symbolism. They often explore themes of faith, hope, love, and suffering.
Prophetic Literature
Prophetic literature includes the books of Isaiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel, Daniel, Hosea, Joel, Amos, Obadiah, Jonah, Micah, Nahum, Habakkuk, Zephaniah, Haggai, Zechariah, and Malachi. These books contain messages from God delivered through prophets. They often address issues of social justice, political oppression, and religious hypocrisy.
Wisdom Literature
Wisdom literature includes Proverbs, Job, Ecclesiastes, and Song of Solomon. These books offer practical advice on how to live a good life. They often explore themes of morality, ethics, and the meaning of life.
Canonical Divisions
The process of canonization in the Old Testament was a gradual one that took place over several centuries. The earliest books of the Hebrew Bible were probably written down in the 10th century BCE, but the canon was not officially closed until the Council of Jamnia in 90 CE.
The criteria used to determine which books were included in the canon were complex and varied. Some of the most important factors included:
Authorship
The books of the Old Testament were believed to have been written by prophets or other inspired individuals. This gave them a special authority that set them apart from other writings.
Antiquity
The books of the Old Testament were also considered to be ancient. This gave them a sense of historical importance and made them more likely to be accepted as authoritative.
Content
The content of the books of the Old Testament was also important. The books that were included in the canon were those that were believed to contain the most important religious teachings.
Modern Divisions

The Old Testament, like other ancient texts, was not originally divided into chapters and verses. These divisions were added later to facilitate reference and study.
The chapter divisions were introduced by Archbishop Stephen Langton in the 13th century, while the verse divisions were added by Robert Estienne in the 16th century. These divisions have since become standard in all printed editions of the Old Testament.
Purpose and Significance
The chapter and verse divisions serve several important purposes:
- They provide a convenient way to refer to specific passages of the Old Testament.
- They help to organize the text and make it easier to navigate.
- They facilitate the comparison of different passages.
The chapter and verse divisions are not without their critics. Some argue that they can lead to a fragmented understanding of the text, since they can break up the flow of the narrative or argument. However, the benefits of these divisions far outweigh their drawbacks, and they have become an indispensable tool for the study of the Old Testament.
Comparative Divisions
The divisions of the Old Testament vary among different religious traditions, reflecting their distinct theological interpretations and historical contexts.
Jewish Tradition
In Jewish tradition, the Old Testament is divided into three main sections:*
-*Torah (Law)
Contains the first five books of the Old Testament, attributed to Moses.
-
-*Nevi’im (Prophets)
Includes historical books (e.g., Joshua, Kings), prophetic books (e.g., Isaiah, Jeremiah), and a book of lamentations (Lamentations).
-*Ketuvim (Writings)
Comprises various literary genres, including poetry (e.g., Psalms, Proverbs), wisdom literature (e.g., Job, Ecclesiastes), and historical narratives (e.g., Chronicles, Esther).
Christian Tradition
In Christian tradition, the Old Testament is typically divided into four main sections:*
-*Pentateuch
The first five books of the Old Testament, similar to the Jewish Torah.
-
-*Historical Books
Includes historical narratives from the conquest of Canaan to the return from Babylonian exile.
-*Wisdom Literature
Comprises books of poetry, proverbs, and other didactic works.
-*Prophets
Includes both major and minor prophetic books, addressing various themes of judgment, hope, and redemption.
Similarities and Differences
The Jewish and Christian divisions of the Old Testament share some similarities, such as the inclusion of the Pentateuch and the prophetic books. However, there are also significant differences:*
-*Order of Books
The order of books within each section varies between the two traditions.
-
-*Inclusion of Books
The Jewish tradition includes the book of Lamentations in the Prophets section, while the Christian tradition places it in the Writings section. Additionally, the Christian Old Testament includes several apocryphal books not found in the Jewish canon.
-*Purpose
The divisions in the Jewish tradition are primarily based on literary genre, while the Christian divisions emphasize theological themes and the fulfillment of prophecy in the New Testament.
These variations in divisions reflect the different ways in which the Jewish and Christian traditions have interpreted and used the Old Testament throughout history.
Popular Questions: Como Se Divide El Antiguo Testamento
What are the three main historical divisions of the Old Testament?
Torah (Law), Nevi’im (Prophets), and Ketuvim (Writings)
What are the four main literary divisions of the Old Testament?
Poetic, Prophetic, Wisdom, and Historical
What is the process of canonization in the Old Testament?
The process by which certain books were selected and included in the official collection of sacred writings based on criteria such as authorship, content, and historical significance.
